Mammography Mammography remains as an irreplaceable point of support in the domain of bosom malignant growth screening, offering a focal point into early identification that can essentially upgrade treatment results and endurance rates. Throughout the long term, progressions in innovation and strategy have pushed mammography from its early stages to a complex demonstrative device, refining its viability and extending its span. This early on investigation dives into the development of mammography, its critical job in bosom disease location, and the contemporary scene of advancements driving its proceeded with refinement.At its center, mammography exemplifies the marriage of clinical science and innovative resourcefulness, upsetting the way to deal with bosom disease recognition since its commencement. The excursion begins with the spearheading endeavors of early radiologists who laid the foundation for mammography’s improvement during the twentieth hundred years. At first restricted to simple strategies, mammography has gone through a transformation moved by the computerized upheaval, introducing a time of uplifted accuracy and openness.The meaning of mammography reaches out past its specialized ability; it exemplifies an encouraging sign for a large number of ladies around the world, offering a proactive position against an illness that has no limits. Through routine screenings, mammography engages people with the information and organization to defy bosom malignant growth head-on, encouraging a culture of early mediation that can be instrumental in checking its effect. Besides, as differences in medical care access endure, mammography arises as a vital device in advancing value, endeavoring to guarantee that all people, paying little heed to foundation or situation, have evenhanded admittance to life-saving screening measures.
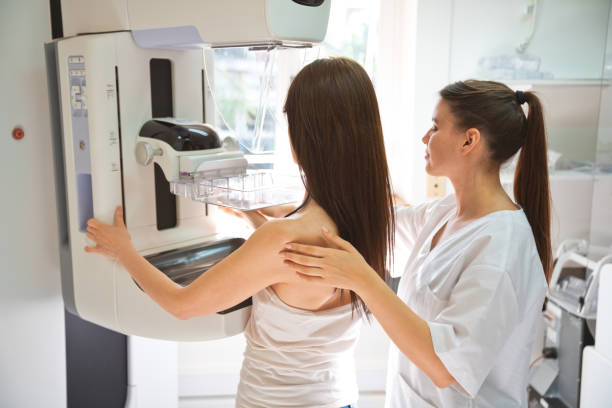

As we explore the multifaceted scene of bosom malignant growth discovery, it becomes clear that mammography possesses a focal situation in our munititions stockpile against this unavoidable sickness. In the following discussion, we decipher the mammography’s many facets, including its effectiveness, difficulties, and the unrelenting pursuit of innovation that propels this essential screening method forward.
Mammography Breast Cancer Screening Cases
In recent years, mammography has established itself as an essential tool for the early detection and treatment of breast cancer. As a harmless imaging method, mammography assumes a vital part in evaluating for bosom disease, empowering medical care experts to recognize irregularities in bosom tissue at a beginning phase, frequently before side effects manifest. The meaning of mammography in bosom malignant growth screening couldn’t possibly be more significant, as early recognition essentially builds the possibilities of effective treatment and further developed results for patients. This passage investigates the different parts of mammography bosom disease screening cases, revealing insight into its significance, difficulties, and headways in the field.
Cases involving mammography breast cancer screening include a wide variety of clinical scenarios. Patients who present with clinical concerns such as breast lumps, nipple discharge, or changes in the appearance of the breasts as well as asymptomatic patients who undergo routine screening to detect any signs of breast abnormalities may be involved in these cases. In the two situations, mammography fills in as an important demonstrative device, giving itemized pictures of the bosom tissue that can help with the recognition and portrayal of dubious sores. Translation of mammography pictures requires specific preparation and aptitude, as radiologists cautiously break down the discoveries to decide the presence of irregularities and survey the probability of threat. While mammography stays the foundation of bosom malignant growth screening, it isn’t without restrictions. Bogus positive and misleading adverse outcomes can happen, prompting superfluous tension or deferred analysis, separately. Furthermore, mammography might be less compelling in specific populaces, for example, ladies with thick bosom tissue, where the understanding of pictures can be trying because of covering structures. Regardless of these difficulties, progressing headways in mammography innovation, like computerized mammography and tomosynthesis, hold guarantee for working on the precision and dependability of bosom disease screening. By persistently refining strategies and conventions, medical services suppliers endeavor to enhance the adequacy of mammography in recognizing bosom disease at its earliest and most treatable stages.

Mammography Bosom Malignant Growth Screening Recognition
Mammography chest threatening development screening ID expects a crucial part in early acknowledgment and coming about treatment of chest illness, the most notable sickness among women all over the planet. This screening procedure incorporates taking low-segment X-pillar photos of the chests, allowing clinical specialists to recognize irregularities, for instance, developments or questionable masses that could exhibit the presence of cancer-causing cells. Standard mammograms are proposed for women, routinely starting at age 40, though the repeat could vary depending upon individual bet components and clinical history. Since mammography empowers clinical experts to analyze bosom disease at its earliest stages, frequently before side effects are obvious, it enormously improves the probability of fruitful treatment and further developed results. Additionally, degrees of progress in development have redesigned the ampleness of mammography, with mechanized mammography now extensively available, offering all the more clear pictures and more definite area.Furthermore, 3D mammography, otherwise called bosom tomosynthesis, gives three-layered perspectives on the bosom tissue, offering considerably more noteworthy precision in identifying irregularities. Notwithstanding its viability, mammography screening has impediments, including the chance of bogus positive or misleading adverse outcomes, which can prompt pointless nervousness or deferred conclusion. In addition, there is a possibility that some women will feel some discomfort during the procedure, but this is usually minor and temporary. To address these constraints and further develop screening results, continuous exploration is centered around creating imaginative advances and approaches, for example, computerized reasoning calculations to help radiologists in deciphering mammograms all the more precisely and productively. Notwithstanding mammography, other screening techniques, like bosom X-ray and ultrasound, might be suggested for ladies at higher gamble or with thick bosom tissue. In general, mammography stays a foundation of bosom disease screening and early location endeavors, assuming a vital part in diminishing death rates and working on the personal satisfaction for ladies all over the planet. Women are empowered to take control of their breast health through regular screenings, which encourage proactive healthcare practices and ultimately save lives.
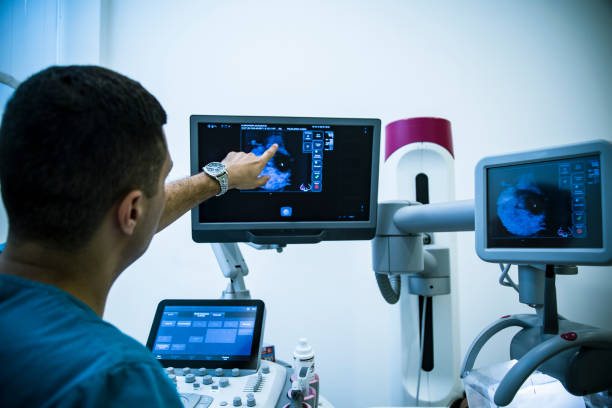
Ultrasound Mammography Breast Cancer Screening
Ultrasound mammography bosom malignant growth screening addresses a promising assistant or option in contrast to customary mammography, especially for ladies with thick bosom tissue or the people who might encounter uneasiness during mammograms. Not at all like mammography, which utilizes X-beams to make pictures of the bosom tissue, ultrasound uses high-recurrence sound waves to deliver itemized pictures, offering a without radiation choice for screening. When it comes to distinguishing between fluid-filled cysts and solid tumors, ultrasound is especially helpful because it can effectively detect abnormalities in the breast, such as masses or lesions. Furthermore, ultrasound can give constant imaging, taking into account dynamic appraisal of dubious regions. While ultrasound isn’t normally utilized as an independent evaluating device for bosom malignant growth identification, it is much of the time utilized related to mammography or as a development to explain discoveries from other screening modalities. In situations where mammography might yield uncertain outcomes, for example, in ladies with thick bosom tissue, ultrasound can offer significant extra data, possibly lessening the requirement for superfluous biopsies or further imaging studies. Because it does not involve being exposed to ionizing radiation, ultrasound is also well-suited for imaging younger women or those who are more likely to develop breast cancer. However, ultrasound also has some drawbacks, such as the fact that its interpretation varies and is dependent on the skill of the operator. In spite of these difficulties, headways in ultrasound innovation, for example, the advancement of robotized bosom ultrasound frameworks and the mix of man-made brainpower for picture examination, hold guarantee for working on the exactness and proficiency of bosom malignant growth screening with ultrasound. In addition, continuous exploration endeavors keep on investigating the job of ultrasound elastography and contrast-upgraded ultrasound in improving the identification and portrayal of bosom sores. In general, ultrasound mammography bosom malignant growth screening addresses an important device in the complete way to deal with bosom wellbeing, offering an option for ladies with explicit requirements or inclinations and adding to the early identification and further developed results of bosom disease.
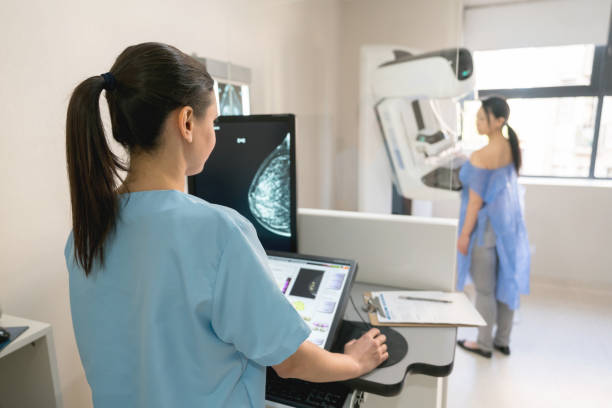
Mammography Versus Breast Cancer Screening
Mammography versus bosom malignant growth screening presents a nuanced conversation in the domain of ladies’ wellbeing, featuring the different modalities accessible for early identification and determination of bosom disease. Mammography, the longstanding highest quality level in bosom malignant growth screening, includes X-beam imaging of the bosom tissue and has been instrumental in distinguishing irregularities at their earliest stages. Its broad use and demonstrated viability in lessening bosom malignant growth mortality highlight its significance in routine evaluating conventions for ladies, normally beginning at age 40. Nonetheless, the limits of mammography, for example, decreased responsiveness in ladies with thick bosom tissue and the potential for bogus positive or misleading adverse outcomes, have provoked investigation into elective screening strategies. For example, ultrasound is a radiation-free option that is especially helpful for women who have dense breasts or who may feel uncomfortable during mammograms. Its capacity to give ongoing imaging and dynamic evaluation of dubious regions supplements the static pictures created by mammography, possibly improving discovery rates and diminishing the requirement for extra subsequent methods. Furthermore, arising innovations like bosom X-ray and atomic bosom imaging (MBI) offer high level imaging capacities that might be used in unambiguous clinical situations, like screening high-risk populaces or assessing ambiguous discoveries from different modalities. While these choices show guarantee in tending to a portion of the constraints related with mammography, they likewise present their own arrangement of difficulties, including cost, accessibility, and fluctuation in translation. Therefore, a thorough evaluation of a patient’s risk factors, breast density, and personal preferences should guide the selection of the most effective screening method, with the aim of maximizing the benefits of early detection while minimizing potential harms. In the end, the debate about mammography versus breast cancer screening is a reflection of the changing landscape of women’s healthcare, which is driven by technological advancements, research findings, and a determination to improve outcomes for all women who are at risk of breast cancer.
Intel Core i7-8700 Processor Explained